Design principles in short-stem total hip arthroplasty
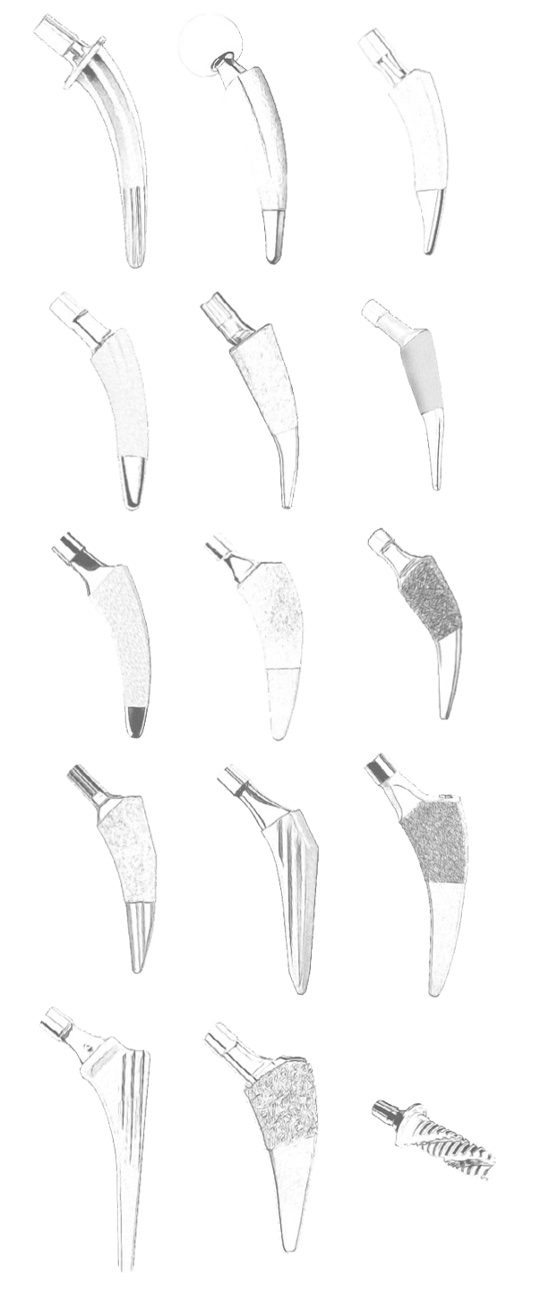
Short-stem total hip arthroplasty is characterized by the use of femoral components with reduced length compared to traditional implants. The design philosophy revolves around achieving stability, preserving bone stock, and optimizing load transfer while addressing the anatomical nuances of the proximal femur. Several key characteristics define short-stem implants. Short-stem implants are engineered to provide stable fixation and efficient load transfer, mimicking the biomechanics of the natural hip joint.


Same same but different: short-stem designs
Characteristics of Short-Stem Total Hip Arthroplasty
The design principles of short-stem total hip arthroplasty (THA) are rooted in the quest for implants that not only address the shortcomings of traditional long-stem designs but also optimize bone preservation, stability, and load transfer. Short-stem implants are characterized by their reduced length compared to traditional counterparts, and their design considerations extend beyond mere size.
One hallmark of short-stem THA is its emphasis on metaphyseal fixation. Unlike long-stem implants that extend into the diaphysis of the femur, short-stem implants engage the cancellous bone of the metaphyseal region. This metaphyseal fixation aims to provide immediate stability, promoting faster bone ingrowth and preserving the natural bone architecture.
The geometry of short-stem implants varies, encompassing straight, curved, tapered, and calcar-guided designs. The choice of design often depends on the surgeon's preference, patient anatomy, and the specific goals of the surgery. These variations in design contribute to the adaptability of short-stem THA, making it suitable for a diverse range of femoral morphologies.
Anatomical Considerations in Implant Design
Anatomical considerations play a pivotal role in short-stem implant design. The goal is to closely mimic the natural anatomy of the proximal femur, ensuring optimal fit, stability, and load transfer. Design features such as curvature, tapering, and calcar preservation are tailored to accommodate the unique anatomical variations observed among patients.
Calcar-guided short stems, for instance, are designed to preserve the calcar region of the femoral neck. This approach prioritizes the maintenance of the femoral neck's natural biomechanical function, promoting stability and load distribution. Implants with modular neck options further enhance the surgeon's ability to customize the implant's fit to the patient's specific anatomy.
The materials used in short-stem implants also contribute to their design principles. Advances in materials science have led to the development of implants made from titanium alloys, cobalt-chromium alloys, and other biocompatible materials. These materials are chosen for their durability, corrosion resistance, and ability to promote osseointegration.
Materials and Manufacturing Advances
The materials and manufacturing processes used in short-stem implants have witnessed significant advancements, contributing to the success and versatility of this approach. Titanium alloys are commonly employed due to their biocompatibility, low modulus of elasticity, and ability to promote bone ingrowth. Additionally, the use of surface coatings, such as hydroxyapatite, further enhances osseointegration.
Manufacturing techniques, including computer-aided design (CAD) and computer-aided manufacturing (CAM), have enabled the production of implants with intricate geometries and tailored specifications. This precision in manufacturing ensures that short-stem implants can be customized to match the unique anatomical characteristics of individual patients.
The continuous evolution of short-stem implant designs, coupled with advancements in materials and manufacturing, reflects a commitment to optimizing the functional outcomes of THA.
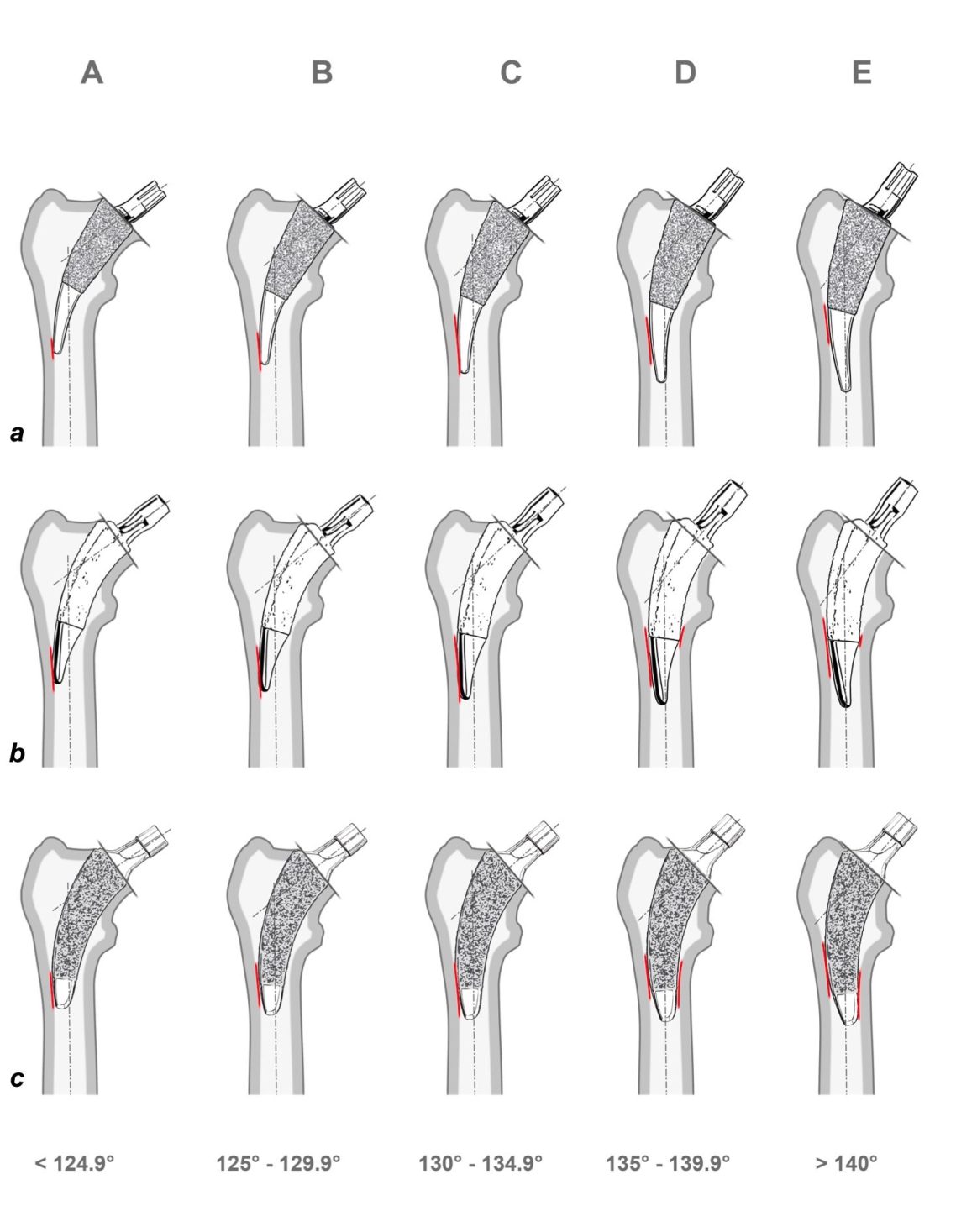

Short-stem THA stands at the intersection of innovation and tradition, challenging conventional norms while preserving the fundamental principles of successful hip arthroplasty. The characteristics of short-stem implants, with their emphasis on bone preservation, metaphyseal fixation, and anatomical alignment, contribute to an evolving paradigm that seeks to optimize patient outcomes.
Wir benötigen Ihre Zustimmung zum Laden der Übersetzungen
Wir nutzen einen Drittanbieter-Service, um den Inhalt der Website zu übersetzen, der möglicherweise Daten über Ihre Aktivitäten sammelt. Bitte überprüfen Sie die Details in der Datenschutzerklärung und akzeptieren Sie den Dienst, um die Übersetzungen zu sehen.