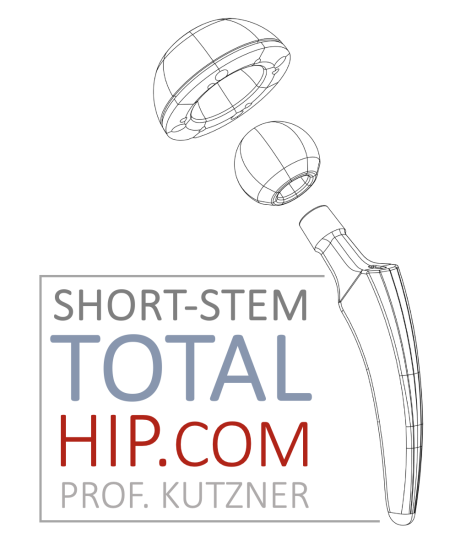
Calcar-guided short-stem total hip arthroplasty
Calcar-guided short-stem total hip arthroplasty represents a promising evolution in hip reconstruction, combining the benefits of short-stem implants with a refined surgical technique. As orthopedic surgeons continue to explore innovative approaches, the calcar-guided technique stands out as a valuable option for those seeking to achieve stability, preserve bone stock, and improve the overall success of total hip arthroplasty. Ongoing research, technological advancements, and clinical experience will further refine and enhance this approach, contributing to the evolution of hip arthroplasty for the benefit of patients worldwide.
Calcar-guided short stems: a contemporary approach to hip reconstruction
Total hip arthroplasty (THA) has witnessed a paradigm shift in recent years, with a focus on innovative techniques that prioritize bone preservation, stability, and improved patient outcomes. Among these advancements, the integration of calcar guidance into short-stem THA has emerged as a notable approach. This chapter explores the principles, benefits, challenges, and future considerations associated with calcar-guided short stems in total hip arthroplasty.
Principles of Calcar-Guided Short Stems
Anatomy of the Calcar: The calcar, a bony ridge on the medial aspect of the femoral neck, plays a pivotal role in hip stability and load transfer. Understanding the anatomy and biomechanics of the calcar is fundamental to the calcar-guided approach.
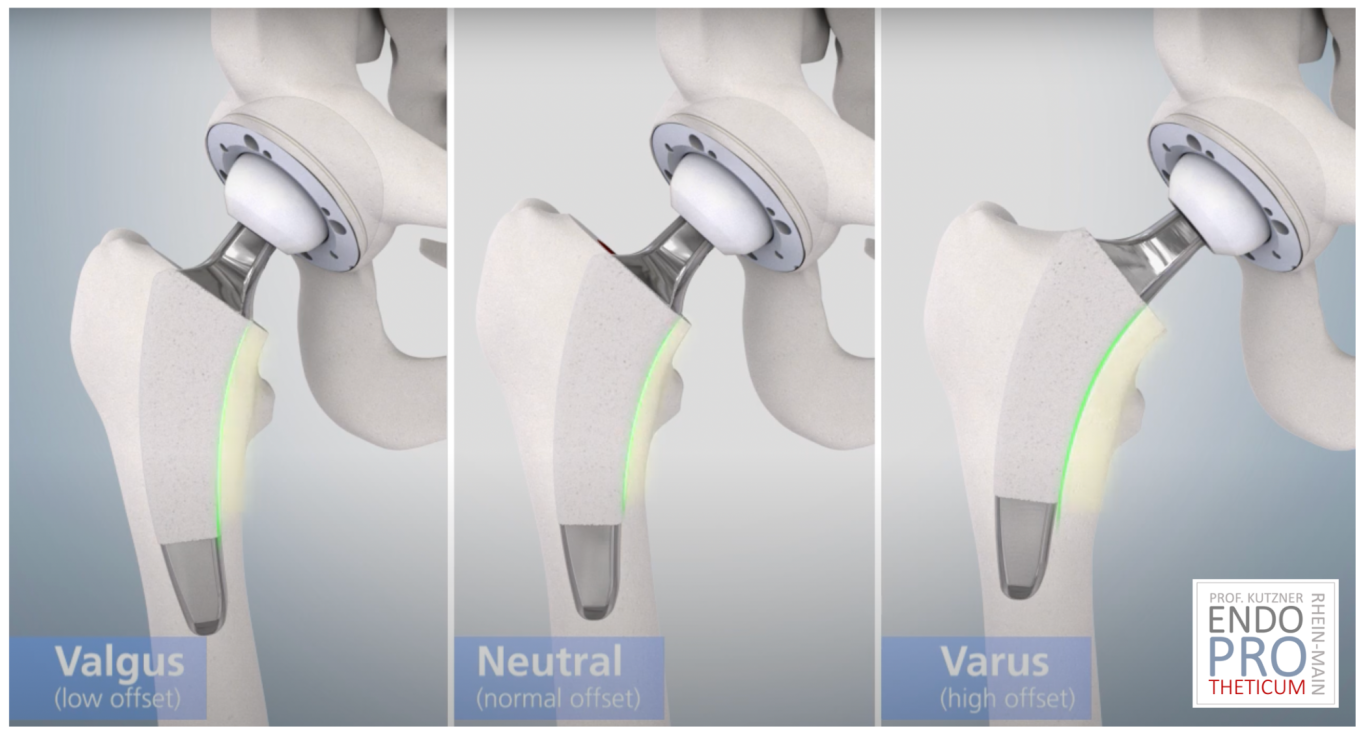
Alignment and Stability: The calcar-guided technique involves aligning the short-stem implant with the medial calcar, optimizing the fit and enhancing stability. Proper alignment aims to replicate the natural hip biomechanics, contributing to improved long-term outcomes.
Advantages of Calcar-Guided Short Stems
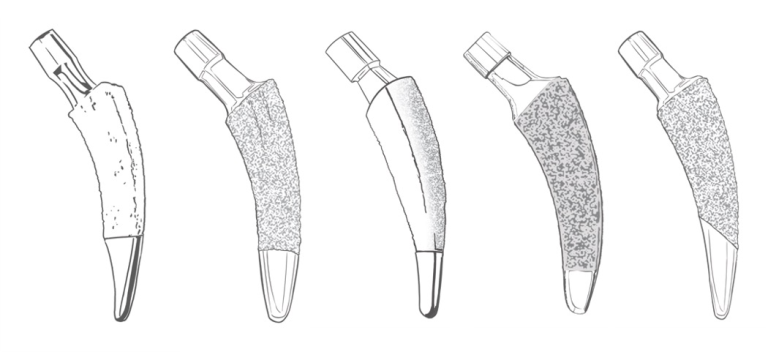
Bone Preservation: One of the primary advantages is the preservation of proximal femoral bone stock. By minimizing bone resection, calcar-guided short stems offer a solution for patients who may require future revisions.
Enhanced Stability: The alignment with the calcar enhances the stability of the implant, reducing the risk of dislocation. Improved stability contributes to a more robust joint reconstruction, particularly in challenging cases.
Optimal Load Transfer: Calcar guidance facilitates optimal load transfer through the femur, reducing stress shielding and the potential for bone resorption. This can enhance the longevity of the implant and improve overall implant survivorship.
Surgical Technique
Patient Selection: Proper patient selection is crucial for the success of calcar-guided short-stem THA. Surgeons need to consider factors such as patient anatomy, bone quality, and individual variability to ensure the suitability of this technique.
Intraoperative Considerations: The surgical procedure involves precise alignment of the short-stem implant with the calcar. Surgeons must be adept at the technique, utilizing imaging guidance and instrumentation designed for calcar alignment.
Challenges and Considerations
Surgeon Expertise: Calcar-guided short-stem THA requires a certain level of surgical expertise. Surgeons adopting this approach should undergo training to master the nuances of calcar alignment and implantation.
Variability in Patient Anatomy: Individual variability in patient anatomy poses a challenge. Surgeons must adapt the technique to accommodate differences in calcar morphology and femoral anatomy.
Clinical Outcomes and Future Directions
Clinical Studies: Ongoing clinical studies and research are essential for evaluating the long-term outcomes of calcar-guided short-stem THA. Comparative studies against traditional methods and other short-stem techniques contribute to a comprehensive understanding of its efficacy.
Technological Advances: Future developments in implant design, surgical instrumentation, and imaging technology may further refine the calcar-guided approach, improving precision and expanding its applicability.
Calcar-guided technique focuses on the proper alignment of the femoral component with the medial calcar of the proximal femur. The calcar, a bony ridge on the medial aspect of the femoral neck, plays a crucial role in providing stability and load transfer in the hip joint. By aligning the short-stem implant with the calcar, surgeons aim to optimize the implant's fit, reduce the risk of complications, and improve overall outcomes.
Advantages of Calcar-Guided Short-Stem THA
1. Preservation of Bone Stock: The calcar-guided approach allows for minimal bone resection, preserving the natural anatomy of the proximal femur. This is particularly advantageous in younger patients or those with good bone quality, as it provides a foundation for potential future revisions.
2. Stability and Load Transfer: Aligning the short-stem implant with the calcar enhances stability and promotes optimal load transfer through the femur. This can contribute to reduced stress shielding, minimizing bone resorption and improving the long-term durability of the implant.
3. Improved Biomechanics: The calcar-guided technique aims to replicate the natural hip biomechanics more closely. By aligning the implant with the calcar, surgeons seek to restore the native hip anatomy, improving joint stability and reducing the risk of complications such as dislocation.
4. Faster Recovery: Short-stem THA procedures, including the calcar-guided approach, are associated with potentially shorter surgical times and less invasive techniques. This may result in reduced tissue trauma, quicker recovery, and shorter hospital stays for patients.

Calcar-guided short-stem total hip arthroplasty represents a promising evolution in hip reconstruction, combining the benefits of short-stem implants with a refined surgical technique. As orthopedic surgeons continue to explore innovative approaches, the calcar-guided technique stands out as a valuable option for those seeking to achieve stability, preserve bone stock, and improve the overall success of total hip arthroplasty. Ongoing research, technological advancements, and clinical experience will further refine and enhance this approach, contributing to the evolution of hip arthroplasty for the benefit of patients worldwide.
Wir benötigen Ihre Zustimmung zum Laden der Übersetzungen
Wir nutzen einen Drittanbieter-Service, um den Inhalt der Website zu übersetzen, der möglicherweise Daten über Ihre Aktivitäten sammelt. Bitte überprüfen Sie die Details in der Datenschutzerklärung und akzeptieren Sie den Dienst, um die Übersetzungen zu sehen.